A control system is defined as a system of devices that directs, controls, or regulates the behavior of devices or other systems to achieve a desired result – It accomplishes this through controlled loops – which are designed to maintain process variables at the desired setpoint.
A control system can always be simplified as one system controlling another system. As human civilization modernizes every day, so does the demand for automation. Automation requires control over the system of interacting devices.
Mechanics Of Control Systems
Control System Terminology:
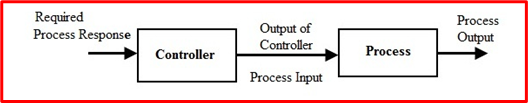
- Controlled process: The part of the system being controlled
- Controller: The part of the system that controls the process.
- Input: The signal given to the system to trigger the command to execute the desired output.
- Output: The desired response to the systems input signal.
- Disturbances: Undesired outputs and variations – failed outputs, faults.
Features of a “Good” Control System:
- Accuracy
Accuracy is the measurement tolerance of the instrument and defines the limit of errors that can be made when the instrument is used under normal operating conditions.
To increase the accuracy, there must be an error detector in the system.
- Sensitivity
Control system parameters are always changing when environmental conditions, internal faults, or other parameters change.
This change can be expressed as sensitivity. Any control system must be insensitive to those parameters, but sensitive only to the input signal.
- Noise Reduction
The unwanted input signal is called noise. A good control system must be able to reduce noise effects for better performance.
- Stability
This is an important characteristic – For a limited input signal, the output must be limited, and if the input is zero, the output must be zero. This is referred to as a stable system.
- Bandwidth
The operating frequency band determines the bandwidth of the system. For a good control frequency response, the bandwidth should be as large as possible.
- Speed
This is the time it takes for the system to reach its steady output. A good control system should have a high speed. The transition period for such a system should be very short.
PDFs / Technicals
Open-Loop vs Closed-Loop Systems
The key difference between an open-loop system and a closed-loop system is that a closed-loop system has the ability to self-correct whereas an open-loop system does not. Therefore, closed-loop systems are often referred to as feedback control systems, while open-loop systems are also referred to as non-feedback control systems.
Features / Examples of this:
- In an open-loop system, the output of the system is independent of the input. In a closed-loop system, the desired output depends on the input.
- An open loop system is called a non-feedback system, while a closed loop system is a feedback system.
- The control and the process being controlled are the two components of an open-loop system.
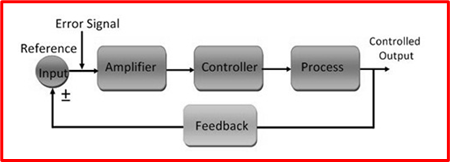
- Closed loops usually require several components like amplifiers, controllers, feedback systems, etc.
- The accuracy of the open-loop system is usually lower than that of the closed-loop system.
- The open-loop system is more stable than the closed-loop system. The word stable here means: The performance of the system remains constant even after disturbances.
- Open-loop systems respond quickly, whereas closed-loop systems respond slowly.
- In an open-loop system, noise affects the output, whereas, in a closed-loop system, the output is less affected by the noise.
Open-Loop Control Systems
What Is an Open-Loop?
With this type of system, the output does not change the operation of the control system in any other way; The open-loop operation is also known as the time-dependent control system.
Advantages
- Simple in design and structure.
- Economical.
- Easy to use and maintain
- Very stable
Disadvantages
- They can’t be trusted because they have less accuracy
- Any change in output cannot be corrected automatically.
Closed-Loop Control Systems
What Is a Closed-Loop?
A closed loop can be defined as a system output that depends on system input. These have one or more feedback loops between their inputs and outputs. It also provides the required output by evaluating the input.
Advantages
- Closed-loop control systems are more accurate even in the presence of abnormality.
- Highly accurate, as any inaccuracies that occur are accounted for by the feedback signal.
- Significant bandwidth coverage.
- It enables automation.
Disadvantages
- They are usually more expensive
- They are complicated in design.
- More support is needed.
Useful Resources
Continued learning..
Dead Shorts, Short Circuits and Ground Faults
Wire Connectors: Sizes, Types, and Charts
Circuit Breaker Basics: Testing, Types and Ratings
How To Test A Motor With A Megohmmeter
Fluorescent Ballasts: What They Do and How