Alternating Current
What is alternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that reverses direction periodically. The waveform of an AC signal is a sine wave, which means that the current changes from positive to negative and back again in a smooth, sinusoidal pattern. AC is the form of electricity that is used in most homes and businesses.
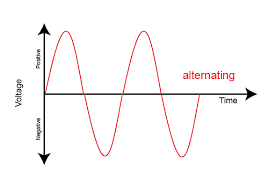
What are the advantages of alternating current
The main advantage of alternating current is that it can be easily transformed to different voltages using a transformer. This allows for long distance transmission of electricity with minimal loss.
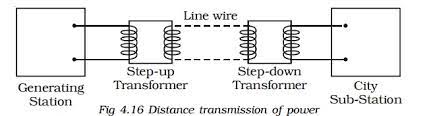
Alternating Current vs Direct Current
The advantages of alternating current over direct current are numerous. Alternating current can be generated more easily and cheaply than direct current. It can also be transmitted over long distances more efficiently than direct current.
Additionally, alternating current can be used to power a wider range of devices than direct current.
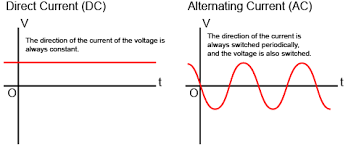
– Direct current is a type of electrical current in which electrons flow in one direction through a conductor, such as a wire.
– Alternating current is a type of electrical current in which electrons flow first in one direction and then in the opposite direction through a conductor.
Direct current is used in a variety of applications, including electroplating, welding, and powering batteries. Alternating current is used in a variety of applications, including electrical power transmission, induction heating, and alternating current motors.
How To Generate Alternating Current
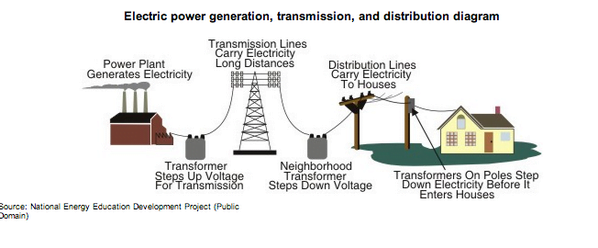
Applications
In the home
- Many small appliances, such as hair dryers and electric shavers, use AC power. Larger appliances, such as clothes washers and dryers, also use AC power.
- AC power is also used to operate lights. Most incandescent light bulbs are designed to work with AC power. Some types of fluorescent lights also require AC power.
In industry
Alternating current is also used in many industrial applications. One example is induction motors, which are widely used in factory settings. These motors rely on AC power to create the magnetic field that rotates the motor shaft.
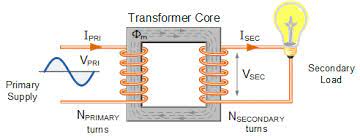
Transformers
How Do Transformers Work?
Transformers work by transferring electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the primary winding and the secondary winding. The primary winding is connected to the power source, and the secondary winding is connected to the load.
– The secondary winding is also a coil of wire wrapped around the same ferromagnetic core.
The primary and secondary windings are inductively coupled, which means that they share a common magnetic field. The primary winding stores energy in the magnetic field, and the secondary winding transfers energy from the magnetic field to the load. This is why a transformer requires alternating voltage (current).
The transformer transfers energy from the primary winding to the secondary winding by electromagnetic induction.
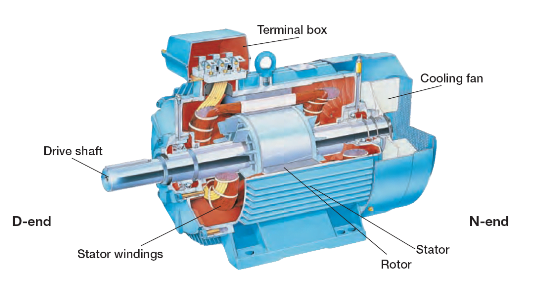
Induction Motors
An induction motor is an AC electric motor in which the electric current in the rotor needed to produce torque is obtained by electromagnetic induction from the magnetic field of the stator winding. The rotor can be either wound type or woundless, permanent magnet type.
The most common type of industrial induction motor is the squirrel-cage rotor
Read More about AC motors here: AC Motors: How Do They Work?
Useful Resources
Alternating Current Fundamentals
Electricity Basics: Ohm’s Law
Suggested Tools: Fluke 323 Multimeter
Electrical Safety: Practical Guide To OSHA & NFPA
FAQ
What is alternating current?
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that reverses direction periodically. This means that the voltage of an AC signal also reverses direction periodically.
The frequency of an AC signal is the number of times per second that the current or voltage reverses direction. Read more..
How does AC differ from DC?
Direct current (DC) is an electric current that flows in one direction only. This means that the voltage of a DC signal does not change over time. DC signals are typically generated by batteries or solar cells.
Alternating current, on the other hand, is generated by power plants and flows through the power grid to homes and businesses. Read more..
What are safety concerns with alternating current?
Alternating current can be dangerous if not used properly. For example, touching a live wire carrying AC can result in electrocution. AC can cause interference in electronic devices, which can lead to data loss or corruption. Read more..