What is 3 Phase Power?
In electricity, a phase is a voltage or current that exists between an active wire and a neutral cable. An oscilloscope, a digital device that plots a graph of the instantaneous signal voltage as a function of time, is used to evaluate the waveform of the electronic signals it is producing.
Additionally, whether a phase is a single-phase or three-phase, its power relies on how its electric load is distributed according to the type of unit.
A single-phase (1 phase) system uses two wires and produces less power than a three-phase (3 phase) system, which uses three or four wires and produces more power.
3-Phase Power
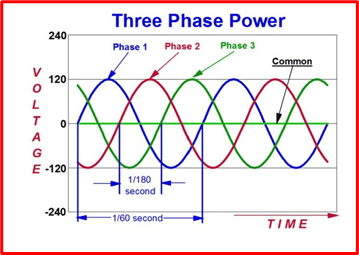
Three-phase power provides three alternating currents, with three separate electric services. Only a third of the way through a whole cycle does each leg of alternating current achieve its maximum voltage. In other words, the power output of a three-phase power source never decreases to zero and remains constant.
There must be four wires in a three-phase power supply, including one neutral wire and three conductor wires. These three conductor wires are 120 degrees apart from one another. Additionally, each AC power signal is 1200 out of phase with the others.

In addition, a three-phase power supply has two distinct circuit designs, the Delta and the Star. Only high voltage systems employ the neutral wire in the Delta Configuration, whereas the neutral wire and ground wire are needed in the Star Configuration.
Books on Amazon for extended learning:
Advantages Of 3 Phase Power
- It runs heavier loads with ease. A three-phase power supply is preferred by commercial and industrial loads since they have heavier electronic loads.
- Three-phase motors, which are commonly used in large businesses, do not need any starters since the phase difference is enough to provide the initial torque needed to start the motor.
- Less conducting materials are needed to transmit and distribute electrical power using a three-phase power source. So, talking about costs makes it more economical.
- The DC voltage of a three-phased power system gets smoother and more beneficial as the number of phases in the system rises.
Disadvantages Of 3 Phase Power
- The three-phase power supplies and motors maintain a high cost of insulation due to the system voltage being fairly high. Insulation is dependent on the unit’s voltage, whereas the size of the wire is dependent on the current.
- Overload cannot be handled by three-phase power units. Meaning that when damage occurs, the cost of repair is higher because replacing individual components is expensive.
Single Phase Power
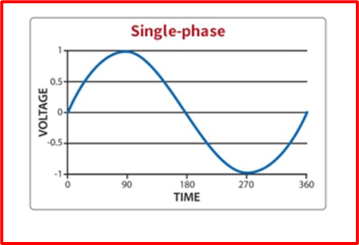
Single-phase power simultaneously modifies the system’s AC power supply voltage. Since the majority of residences use single-phase power, it is more commonly referred to as “residential voltage.”
It generates a single sine wave (low voltage). 230V serves as the starting point for the common voltage for single-phase power. Additionally, it has a frequency that is similar to 50Hz.
Due to the lack of a rotating magnetic field produced by a single-phase supply connected to an AC motor, single-phase motors need additional circuitry to function. A single-phase supply’s voltage supply fluctuates since the power output is not consistent
Differences Between Single Phase vs Three Phase Power
- Required Wiring On Power Supply
There are only two wires needed in a single-phase power supply: the phase and neutral wires. On the other hand, a three-phase power supply simply utilizes three wires—a neutral wire and two three-conductor wires—to function.
Consequently, when you deliver three-phase power directly to your server cabinets, both the expenses of cabling and overall installation are decreased.
- Voltage
It only supports 230V in a single-phase power supply while reaching its maximum in a three-phase power supply at 415V.
- Use-Cases
Residential homes often use a lower power supply, requiring less energy to run your mobile devices and home equipment. Commercial and industrial businesses, on the other hand, demand a greater electronic burden. As a result, they run on a three-phase power supply.
- Application
While a three-phase power supply powers power grids, data centers, aircraft, ships, and other electronic loads more than 1,000 watts, a single-phase power supply produces less electricity to support residences and non-industrial enterprises.
- Consistency Of The Delivery Of Power
Due to the peaks and dips in voltage, a single-phase power supply does not offer the same consistency as a three-phase power supply. A three-phase power supply delivers power at a steady, constant rate.
- Efficiency
Three-phase power supplies are more efficient. A three-phase power supply can transmit three times as much power as a single-phase power supply, while only needing one additional wire (that is, three wires instead of two). Thus, three-phase power supplies, whether they have three wires or four, use less conductor material to transmit a set amount of electrical power compared to single-phase.
Video Explainer
Useful Resources
Continued Learning:
Understanding Step Up and Step Down Transformers
Fault Interrupters: AFCI vs GFCI
The Difference Between an Alternator vs Generator
FAQs
What is the difference between 1 phase and 3 phase power?
The main difference between 1 phase and 3 phase power is the number of conductors used to transmit the electrical energy. 1 phase power has one live conductor and one neutral conductor, while 3 phase power has three live conductors and one neutral conductor. This difference in the number of conductors affects the way the power is delivered, and the types of equipment that can be used to receive and utilize the power.
What is the benefit of 3 phase power?
One of the main benefits of 3 phase power is its ability to deliver more power with less current. This means that 3 phase power is more efficient than 1 phase power, and can be used to power larger equipment and machinery. 3 phase power is also more reliable, as it provides a constant, even supply of power, which reduces the risk of power surges and brownouts.
What is the most common 3 phase power?
The most common 3 phase power used in industrial and commercial settings is 208 volts, which is a type of low voltage 3 phase power. However, higher voltage 3 phase power is also used in some applications, such as 480 volts or 600 volts.
Is 3-phase electricity more expensive?
The cost of 3-phase electricity depends on a variety of factors, such as the amount of power used, the location, and the supplier. In some cases, 3-phase electricity may be more expensive than 1 phase electricity, while in other cases it may be less expensive. It is best to check with your local utility provider for specific pricing information.
What is 3-phase power for?
3-phase power is used in a variety of industrial and commercial applications to power large equipment and machinery. It is also used in some residential settings for high-power appliances such as electric ranges, air conditioning units, and hot tubs. 3-phase power is known for its efficiency and reliability, which makes it an ideal choice for powering high-power devices.