Alternator Vs Generator – The Differences Explained
When most people think of a generator, they typically picture a portable generator that they might use as a backup for their home and when we talk about alternators, the next thing that comes to our mind is that device that powers our car battery.
These comparisons are accurate, but it’s important to know the technical variations in how these devices produce electricity and supply our homes and vehicles with power.
What Is An Alternator?
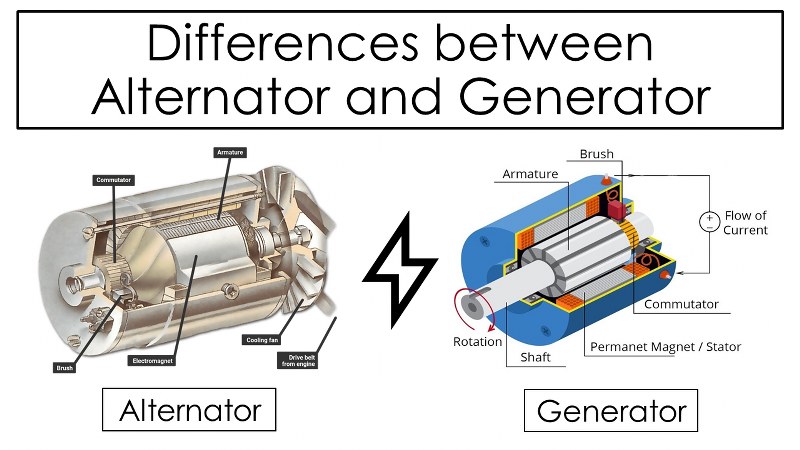
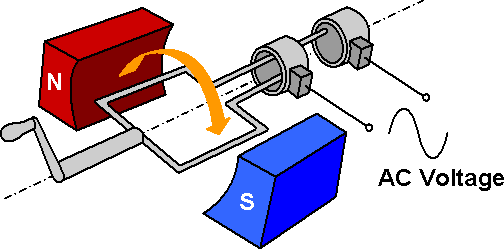
An alternator is a device that creates alternating current by transforming mechanical energy into electrical energy. As a result, it is also known as an AC generator or Synchronous generator.
How an Alternator Works
In an alternator, the magnetic field (rotor) revolves around the armature (stator). Using a DC supply, a permanent magnet or an electromagnet produces the magnetic field. The housing that encloses the armature is the electromagnet. Steam turbines, gas turbines, and combustion engines are all examples of prime movers that can spin the magnetic field. The change in the magnetic field lines crossing the armature conductors is brought about by its rotation. The armature is consequently given out an electric current.
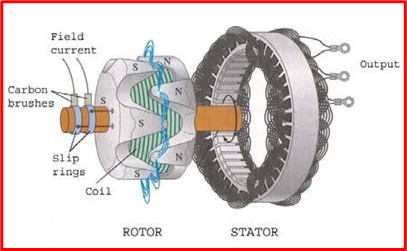
Electric current is delivered to the output load by the armature through brushes. The brushes never wear out since the armature is constant. This lengthens its mechanical life and lowers the need for maintenance.
When operating on the stationary armature, the rotating magnetic field continuously flips its polarity (from north to south), which results in a continuous shift in the direction of the induced current. The alternator’s output is always alternating current as a result of this.
What Is a Generator?
Just like alternators, generators transform mechanical energy into electrical energy. The mechanism involved is similar to that of an alternator, but a generator can deliver either direct current or alternating current (AC or DC).
How a Generator Works
The generator’s outer casing, which encloses the armature, is built of either a permanent magnet or the stator ( a stationary electromagnet). Within this stationary magnetic field, the armature, which is composed of conductor coils, rotates about its axis. The location of the magnetic field line where the conductors intersect changes as a result of the rotating armature. As a result, the rotating armature induces a current.
Either a commutator or a slip ring is used to join the armature. The electric current, which is constantly changing direction, is transferred by both of them from the revolving armature to the static output circuit. The slip ring, however, has a complete circular connection that enables the continuous flow of the electrical current from the rotating shaft, producing AC (alternating current). The output current, often referred to as Direct Current (DC), stays in one direction because the commutator, which has at least two breaks between them, changes the direction of the current after each half rotation.
The Differences Between an Alternator vs Generator
Below are the distinctions between an alternator and a generator:
- An alternator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into AC electrical energy, while a generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into either AC or DC electrical energy.
- An alternator can only generate alternating current (AC) while a generator can generate either Direct Current (DC) or Alternating Current (AC).
- In an alternator, the rotating part or rotor is the magnetic field, while in the generator the rotating part or rotor is the armature.
- In an alternator, the stator is used to draw the output current that is generated while in a generator, the rotor is used to draw the output current generated
- Compared to generators, alternators have a higher output current.
- The brushes used in alternators last longer because the armature is stationary and there is no friction, whereas, in generators, the brushes wear out due to friction against the rotor, thus they do not last very long.
- A battery that is entirely dead can be charged by a generator while an alternator can never charge a dead battery.
- After installation, an alternator does not need to be polarized while the generator needs to be polarized after installation.
- Alternator serves as a battery charging method in the automobile industry while generators are frequently utilized to generate significant amounts of electricity.
Useful Resources
FAQs
How does an AFCI work?
AFCIs work by sensing when an arc fault is about to occur and then interrupting the flow of electricity before the arc can form. Read more..
How to use Ohm’s Law?
Ohm’s law is used in many branches of physics, including electricity, magnetism, and optics. It can be used to design electrical circuits, calculate power dissipation in electronic devices, and troubleshoot electrical problems. Read more.
What are safety concerns with alternating current?
Alternating current can be dangerous if not used properly. For example, touching a live wire carrying AC can result in electrocution. AC can cause interference in electronic devices, which can lead to data loss or corruption. Read more..