Synchronous Motors Explained
What are synchronous AC motors?
A synchronous AC motor is an electric motor that uses alternating current (AC) to produce rotational force. Unlike an asynchronous AC motor, a synchronous AC motor rotates at the same speed as the frequency of the AC power supply.
In order to achieve this, the synchronous AC motor must be synchronized with the power supply using a feedback system.
Synchronous AC motors are typically used in applications where constant speed is required, such as in clocks and turntables.
Additionally, synchronous AC motors are often used as generators, since they can be easily synchronized with an external power source.
For additional information on AC motors read: AC Motors: How Do They Work?
Benefits of synchronous motors
One of the biggest benefits of a synchronous AC motor is its high efficiency. Because there is no slip between the rotors and the stator, this type of motor does not waste energy through heat loss.
Additionally, synchronous motors are relatively simple to construct and maintain, which makes them more affordable than other types of motors.
Finally, synchronous AC motors can be controlled very precisely, making them ideal for use in applications where precise positioning is required. Overall, the benefits of a synchronous AC motor make it an attractive option for a wide range of applications.
Single Phase synchronous motors
A single phase synchronous motor is a type of electric motor that uses alternating current (AC) to produce rotational force.
The key difference between a single phase synchronous motor and other AC motors is that it uses a permanent magnet (or electromagnet) to create a rotating magnetic field.
This rotating field interacts with the stator, or stationary portion of the motor, to create torque that causes the rotor to rotate.
In order for a single phase synchronous motor to work, it must be electrically polarized, meaning that its poles must be oriented in opposite directions. Once the poles are aligned, the current can flow through the rotor, causing it to rotate.
3-phase synchronous motors
A three-phase synchronous motor can operate at both constant speed and variable speed. Constant speed operation is achieved by using a three-phase power source with a frequency that matches the rated speed of the motor.
Variable speed operation is achieved by using a three-phase power source with a variable frequency.
Three-phase synchronous motors are used in a variety of applications, including:
- pumps
- compressors
- fans
- conveyors
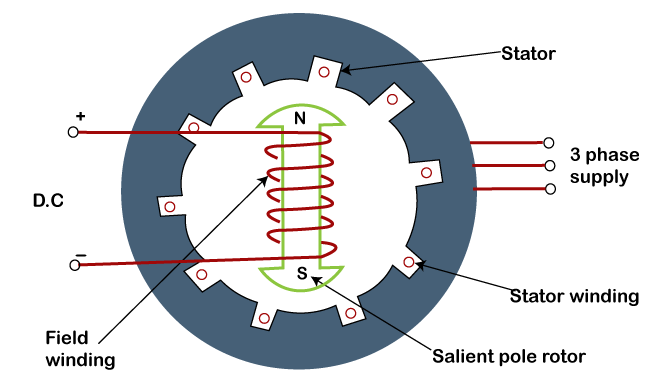
When current is applied to the stator windings, it creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the magnetic field of the rotor, causing the rotor to rotate. The speed of the rotation is determined by the frequency of the current, and the torque is determined by the strength of the magnetic field. By carefully controlling the stator current, it is possible to create a motor with very high efficiency and reliability.
Useful Resources
Synchronous Motors and Special Purpose Motors
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors
The Difference Between an Alternator vs Generator
FAQs
How to identify a broken light switch?
The first step in knowing how to fix a broken light switch is being able to identify when one exists. There are a few telltale signs that a light switch may be broken, which include:
-The switch does not click when engaged.
-The switch feels loose or wobbly.
–Read more..
What is Ohm’s Law?
Ohm’s law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points. In other words, the higher the voltage, the higher the current. Read more..
What is an AC motor?
An AC motor is an electric motor that uses alternating current (AC) instead of direct current (DC). AC motors are more efficient than DC motors and can be found in a variety of applications, including fans, pumps, and compressors. Read more..