AFCI vs GFCI:
What’s the difference?
What is an arc fault circuit interrupter (AFCI)?
An arc fault circuit interrupter (AFCI) is a type of circuit breaker that is designed to protect against electrical fires caused by arcing faults.
Arcing faults occur when electricity jumps or arcs across an air gap and can cause sparks or even flames.
AFCIs are designed to detect these types of faults and then interrupt the electrical circuit to help prevent a fire from starting.
Need help with the basics?
Try these articles: Alternating current explained, Direct current explained, Ohm’s Law
How does an AFCI work?
AFCIs work by sensing when an arc fault is about to occur and then interrupting the flow of electricity before the arc can form. This prevents electrical fires from starting and can save lives.
AFCIs are typically installed in homes as part of the electrical system and can be added to existing circuit breakers or installed as new circuit breakers.
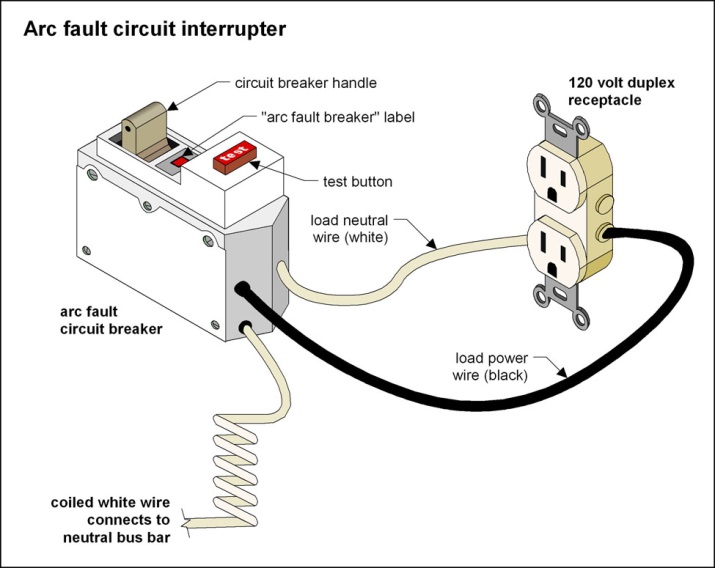
What is a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI)?
Related Articles: GFCI outlet wiring, How to replace electrical outlets
A ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) is a type of circuit breaker that is designed to protect against electrical shocks caused by ground faults. Ground faults occur when electricity jumps or arcs across an air gap and can cause sparks or even flames.
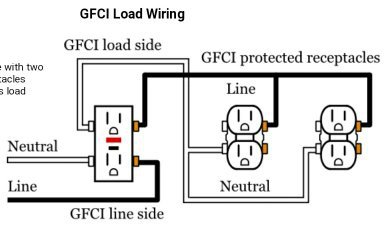
GFCIs are designed to detect these types of faults and then interrupt the flow of electricity before the arc can form. This prevents electrical shocks from occurring and can save lives.
GFCIs are typically installed in homes as part of the electrical system and can be added to existing circuit breakers or installed as new circuit breakers.
How do AFCIs and GFCIs work?
How do AFCIs and GFCIs work differently to prevent electrical fires in the home?
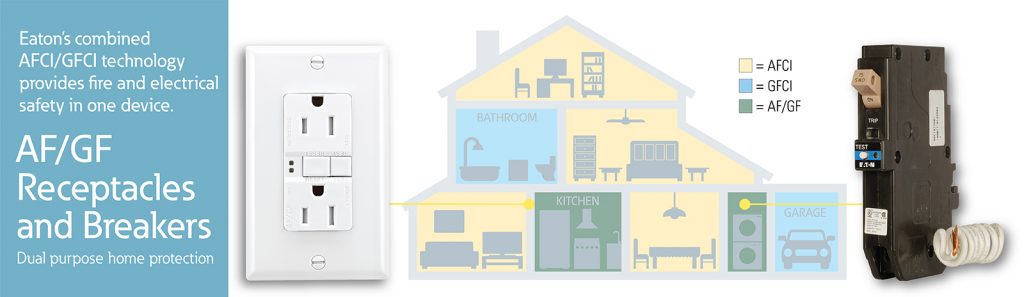
AFCIs work by sensing when an arc fault is about to occur and then interrupting the flow of electricity before the arc can form. This prevents electrical fires from starting and can save lives. GFCIs work by sensing when a ground fault is about to occur and then interrupting the flow of electricity before the fault can cause an electrical shock.
This prevents electrical shocks from occurring and can save lives. Both AFCIs and GFCIs are designed to protect against the dangers of electrical fires and shocks, and both should be installed in homes as part of the electrical system.
How can you tell if an AFCI or GFCI is working properly?
You can test an AFCI or GFCI by using a circuit tester or multimeter. Simply plug the tester into an outlet and touch the probes to the hot and neutral wires. If the tester lights up, the AFCI or GFCI is working properly. If the tester does not light up, the AFCI or GFCI may be damaged and should be replaced.
What should you do if your AFCI or GFCI trips?
If your AFCI or GFCI trips, it means that it has detected an arc fault or ground fault and interrupted the flow of electricity to prevent an electrical fire or shock. You should check your electrical system to make sure there are no damaged wires or other potential hazards before resetting the AFCI or GFCI.
If your AFCI or GFCI trips frequently, you may need to have your electrical system inspected by a qualified electrician.
Fault interrupters: Home Safety
How can you tell if your home’s electrical wiring needs to be updated or replaced altogether?
Try these articles for more help: How to wire 3-way switch, Convert 3-way switch to single pole, Understanding open neutrals
If your home’s electrical wiring is more than 40 years old, it may need to be updated or replaced. Look for signs of wear and tear, such as frayed or exposed wires, or outlets that don’t work. If you notice any of these issues, call a qualified electrician to inspect your electrical system and make any necessary repairs. Updating or replacing your electrical wiring can help prevent electrical fires in the home.
FAQs
What are the benefits of AC motors?
AC motors are more efficient than DC motors and can operate at higher speeds. Additionally, AC motors are less likely to overheat than DC motors and can be used in a variety of applications. Read more..
What is an arc fault circuit interrupter (AFCI)?
An AFCI is a type of circuit breaker that is designed to protect against electrical fires caused by arcing faults. Read more..
How does and AC motor work?
An AC motor works by using electromagnetism to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. The alternating current creates a rotating magnetic field that interacts with the armature, or rotor, of the motor to create torque. Read more..