Is a Diode a Rectifier?
Diodes are semiconductor devices that allow current to flow in only one direction, making them useful for a variety of applications such as rectification, voltage regulation, and signal modulation. The term “rectifier” refers to the diode’s ability to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC).
This is accomplished by allowing current to flow through the diode during the positive half-cycle of the AC signal while blocking the negative half-cycle. As a result, the output DC signal is equivalent to the average value of the input AC signal. Diodes are also used in power supplies to convert AC power into DC power.
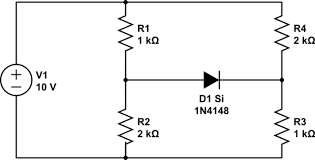
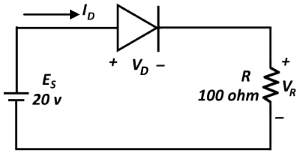
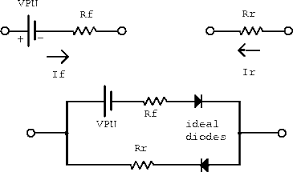
In this application, a group of diodes is used to rectify the AC input signal, producing a DC output signal with much higher voltage. Rectifier diodes are also used in electronic circuits to limit or clamp the voltage level to a desired value. A variety of diodes are shown here:

By allowing only positive voltage peaks through the diode, unwanted negative voltages can be prevented from damaging sensitive electronic components.
For a deeper understanding of rectification and how rectifiers work: Troubleshooting Rectifiers: Intro to Circuits and Diodes
Video Explainer
The video below takes a deeper dive into how exactly diodes work and some of the different types of diodes, such as: Zener Diodes, Schottky Diodes, Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs), and Photodiodes.
PDFs / Technicals
Semiconductor Diodes – Learn About Electronics
Recommended Tools:
Diode Polarity
While a diode’s polarity may seem like a small detail, it’s actually quite important. The polarity of a diode determines the direction in which current can flow.
If the diode is connected with the wrong polarity, it will block current rather than allow it to flow. As a result, it’s essential to pay attention to the polarity when connecting a diode.
There are two ways to identify the polarity of a diode.
- The first is to look for a stripe on the body of the diode. This stripe indicates the cathode, or negative, side of the diode.
- The other way to identify polarity is to use a multimeter.
When testing a diode with a multimeter, you’ll need to connect the leads to the two different sides of the diode. The positive lead should be connected to the anode, or positive, side of the diode.
- If the multimeter reads “0,” then the diode is connected with the correct polarity.
- If it reads “1” or “OL,” then the diode is connected with reversed polarity and will need to be corrected.
Diode Circuits
Types of Diodes
- Rectifier Diodes
Rectifier diodes are utilized to convert AC power into DC power by allowing only positive voltage peaks through while blocking out negative voltages that could potentially damage sensitive electronic components or systems that draw their power from DC sources only (and not AC sources).
The diodes work by forming a bridge between two terminals on either side of an electrical circuit; when forward-biased with electricity entering from one side, then leaving via another side after passing through the diode’s junction barrier and getting rectified; this enables DC power to be drawn from an AC source without any interference from unwanted voltages or frequencies that could disrupt or damage other components connected to it.
Applications:
Power supplies used for numerous applications often require transforming AC power into DC before it can be used; this is where rectifier diodes shine as they make this possible efficiently and reliably by preventing negative voltages from interfering with other components present in the system while allowing desired positive voltages to pass through unhindered thus providing clean uninterrupted DC power output when supplied with adequate AC input signals at regular intervals and cycles.
- Light Emitting Diodes
An LED is a semiconductor light source that emits visible light when an electric current passes through it. LEDs are typically made of gallium, arsenic, and phosphorus or a combination thereof and can produce light in different colors depending on the materials used. They are highly energy efficient and do not require any additional components such as a heat sink or cooling fan to operate properly.
- Zener Diodes
A Zener diode is another type of diode that is operated in reverse bias and can provide a stable reference voltage. Zener diodes are often used in voltage regulation applications where their low forward voltage drop provides more efficient power dissipation than other diodes. Additionally, Zener diodes have the ability to protect against overvoltage conditions by clamping the output voltage to a safe level.
- Schottky Diodes
Schottky diodes have a lower forward voltage than other silicon PN junction diodes and are commonly used in rectifier applications such as dc-dc converters and motor drive circuits. They have very fast switching speeds due to their low capacitance values which also reduces power losses in high frequency switching circuits.
- Photodiodes
Photodiodes are reverse bias diodes that detect even small amounts of current flow resulting from light exposure and can be used for sensing motion, detecting radiation levels, or measuring ambient lighting conditions. They typically consist of two layers of semiconductor material joined together with one layer being heavily doped while the other is lightly doped so that when exposed to light, electrons are injected into the lightly doped layer creating an electrical current which can then be measured or used as part of another circuit such as an amplifier circuit.
Useful References
DC Power Circuit: Direct Current Explained
What Is AC Power: Alternating Current
Practical Electronics for Inventors
FAQ
What is the polarity of a diode?
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that has a polarity. One end of the diode is called the anode, and the other end is called the cathode.
How do you know which way a diode goes?
To determine which way a diode goes, you need to look at its markings. Usually, the cathode side is marked with a stripe or a bar. The stripe or bar on the diode package indicates the end of the diode that corresponds to the cathode.
What is a diode used for?
A diode is used to allow the flow of current in only one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. It is used in a variety of applications, such as rectification, voltage regulation, signal demodulation, and circuit protection.
What does a diode do to a signal?
A diode can modify a signal by allowing only part of it to pass while blocking the rest. This property is used in circuits to remove unwanted parts of a signal, to rectify a signal, or to regulate voltage.
Is an LED a diode?
Yes, an LED (light-emitting diode) is a type of diode that emits light when current flows through it. LEDs are widely used in lighting applications, displays, and indicators.