A centrifugal switch, also known as a centrifugal starter, is a device that is used to automatically start and stop an electric motor. It works by utilizing the centrifugal force that is generated by the rotation of the motor’s rotor.
Main Uses
Centrifugal switches are primarily used in electric motors that are used in appliances such as air conditioners, refrigerators, and other equipment that requires a constant speed. They are also used in industrial settings such as pumps, fans, and other types of machinery.
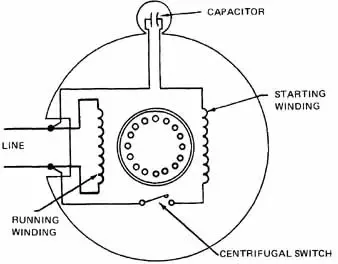
Important note: The centrifugal switch is used in many single phase induction motors to start the motor and change the direction of rotation. It works on the principle of centrifugal force. Once the motor reaches a certain speed, the centrifugal force causes the weights to move outwards, which in turn opens the contact points and stops the motor.
How it Works
As the motor’s rotor begins to rotate, the weights attached to the lever start to move outward due to centrifugal force. This movement causes the lever to trip the switch, which in turn starts the motor.
Once the motor reaches its full speed, the weights continue to move outward, which causes the lever to trip the switch again, disconnecting the starting winding and connecting the running winding.
Parts of a Centrifugal Switch
A centrifugal switch typically consists of a switch, a lever, and a set of weights that are attached to the lever. The switch and lever are located in the motor’s housing, while the weights are attached to the rotor.
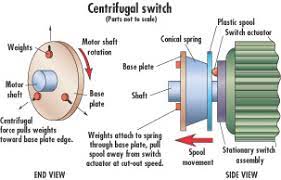
- The contact points: These are the electrical connections that close and open to start and stop the motor.
- The spring: This component provides the tension necessary to keep the contact points closed while the motor is running.
- The centrifugal weights: These weights are attached to the end of a rotating arm and move outward as the motor’s speed increases, ultimately causing the contact points to open and stop the motor.
- The cam: This component is connected to the centrifugal weights and rotates with the arm, pushing the contact points open when the weights move outwards.
- The housing: This encloses and protects the other components of the switch.
- The shaft: This component connects the switch to the motor, allowing it to rotate with the motor’s movement.
- The adjustment screw: This allows for fine-tuning of the switch’s operation, such as adjusting the speed at which the contact points open.
- The lead wires: These are the electrical connections that provide power to the switch and allow it to communicate with the rest of the motor’s control system.



Benefits of Using a Centrifugal Switch
- Uniform Start-up Processes for Motors
Centrifugal switches provide a uniform start-up process for motors, which helps to ensure that the motors are started in a consistent and controlled manner. This can help to prevent damage to the motors and prolong their lifespan.
- Low Production Costs and Minimal Components
Centrifugal switches are relatively simple in design and are made up of minimal components. This makes them relatively inexpensive to produce, which can help to keep production costs low.
- Enhances Performance and Efficiency in Motors
By providing a consistent and controlled start-up process, centrifugal switches can help to improve the performance and efficiency of motors. This can help to reduce energy consumption and prolong the lifespan of the motor.
- Prevents Motor Failure and Overheating
By disconnecting the starting winding and connecting the running winding at the appropriate time, centrifugal switches can help to prevent motor failure and overheating, which can prolong the lifespan of the motor.
Testing
What a Test Entails:
Testing a centrifugal switch involves checking the switch’s ability to trip and reset at the appropriate speeds. This can be done using a multimeter or other testing equipment.
Steps to Follow When Testing a Centrifugal Switch:
- Disconnect the motor from the power source
- Check the switch’s continuity by measuring the resistance between the switch’s terminals
- Rotate the motor’s shaft by hand to simulate the motor’s running speed
- Check the continuity again to ensure that the switch has tripped and reset
- Repeat steps 3 and 4 at different speeds to ensure that the switch is tripping and resetting at the appropriate speeds.
Common Issues
- Not Opening When Needed Can Lead to Overheating in the Start Winding
If a centrifugal switch fails to open when needed, it can lead to overheating in the start winding. This can cause damage to the winding and shorten the lifespan of the motor.
- Not Disconnecting After Motor Starts Can Lead to Failure in the Starting Winding and Overheating in the Main Winding
If a centrifugal switch fails to disconnect after the motor starts, it can lead to failure in the starting winding and overheating in the main winding.
This can cause significant damage to the motor and reduce its efficiency.
Types of Motors That Do Not Contain a Centrifugal Switch
The most common types of motors that do not contain a centrifugal switch: the capacitor-start capacitor-run split-phase motor and the Permanent Split Capacitor (PSC) Motor.
Capacitor-Start Capacitor-Run Split-Phase Motor
The capacitor-start capacitor-run split-phase motor is a type of motor that uses a combination of capacitors to control the speed of the motor. The motor is designed to start with a high initial torque, which is achieved by using a start capacitor. Once the motor is running, the run capacitor is used to maintain a steady speed. This type of motor is commonly used in applications such as fans, blowers, and pumps.
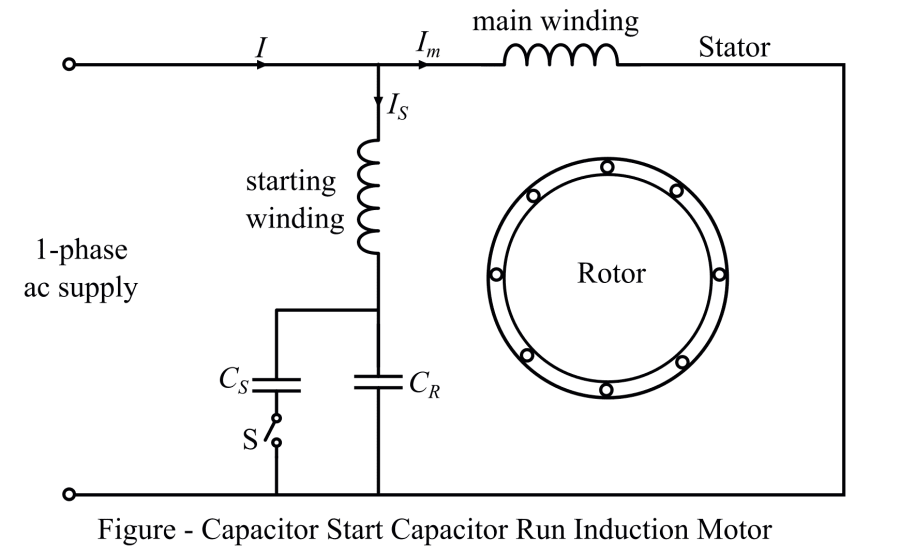
One of the main advantages of the capacitor-start capacitor-run split-phase motor is that it is relatively inexpensive to manufacture and maintain. Additionally, this type of motor is relatively simple to control, making it a popular choice for many applications. However, one of the main disadvantages of this type of motor is that it is not as efficient as other types of motors, which can result in higher energy costs over time.
Permanent Split Capacitor (PSC) Motor
The Permanent Split Capacitor (PSC) motor is another type of motor that does not contain a centrifugal switch. This type of motor uses a single capacitor to control the speed of the motor. The capacitor is permanently connected to the motor, which allows for a steady and consistent speed. The PSC motor is commonly used in applications such as fans, blowers, and pumps.

One of the main advantages of the PSC motor is that it is relatively simple to control, making it a popular choice for many applications. Additionally, this type of motor is relatively inexpensive to manufacture and maintain. However, one of the main disadvantages of the PSC motor is that it is not as efficient as other types of motors, which can result in higher energy costs over time.
PDFs / Technicals
Single Phase Induction Motor Centrifugal Switches
Centrifugal Switch Replacement
(Video) How They Work
Useful Resources
Continued learning..
Choose The Right Motor Starter – Types and How They Work
Phase Monitoring Relays: How They Work
FAQ
What is the purpose of a centrifugal switch?
A centrifugal switch is an electrical switch that is used to control the operation of motors. Its primary purpose is to automatically disconnect the starting winding of a motor once it has reached a certain speed.
What happens if the centrifugal switch does not open?
If the centrifugal switch did not open, the starting winding would remain energized, which can cause the motor to overheat and eventually fail.
Where is a centrifugal switch located?
The location of a centrifugal switch depends on the type of motor. In most cases, it is located inside the motor housing, near the end of the motor shaft.
Do all motors have a centrifugal switch?
No, not all motors have a centrifugal switch. It is typically found in single-phase induction motors and is not commonly used in other types of motors.
How does a centrifugal switch open?
The centrifugal switch is designed to be operated by centrifugal force, which is generated when the motor reaches a certain speed. Once this happens, the switch opens and disconnects the starting winding from the circuit. The switch is typically spring-loaded, so it will close again when the motor stops and the centrifugal force is no longer present.