How to change an outlet
If your outlet is damaged, it may need to be replaced. Damaged outlets can pose a serious fire hazard. If you see any of the following signs, it’s time to replace your outlet:
• The outlet is cracked or broken.
• The outlet shows signs of burns or charring.
• The outlet is loose in the wall.
• There are sparks coming from the outlet.
To understand how to protect circuits check out: AFCI’s vs GFCI’s for an in-depth explanation.
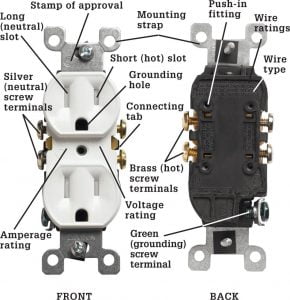
What You’ll Need to Replace an Outlet
How to Replace an Electrical Outlet.
Start by turning off the power to the outlet at your breaker box. Flip the switch to the “Off” position, and then test the outlet to make sure that it’s not live by using a circuit tester. If you don’t have a circuit tester, you can also use a lamp or other small appliance — as long as it’s plugged into another outlet that you know is working.
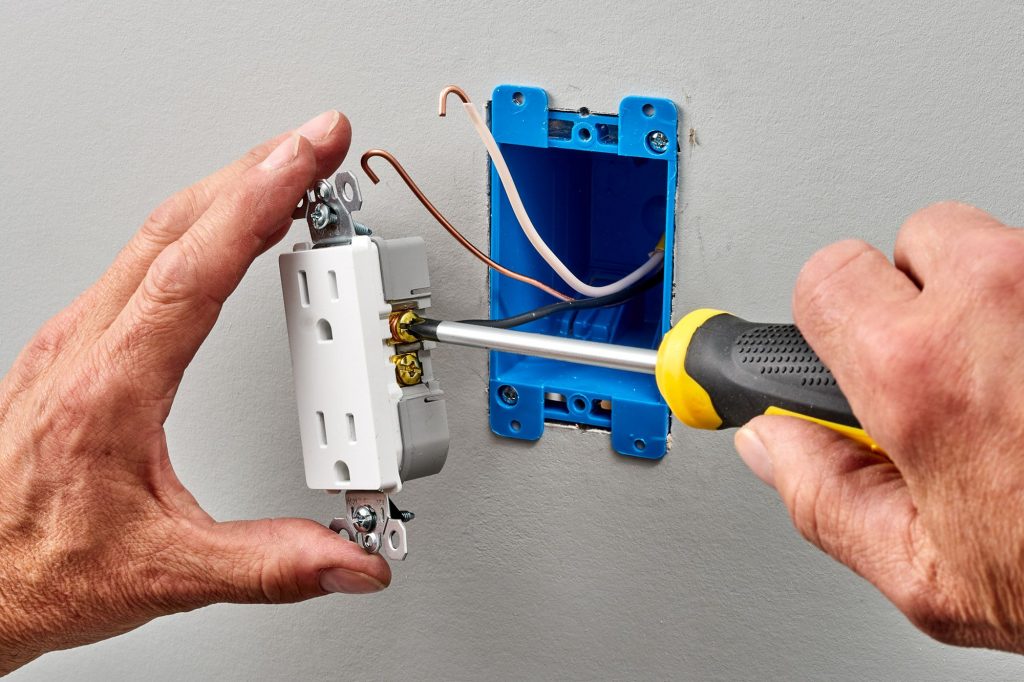
Once you’ve confirmed that the power is off, remove the old outlet. Start by removing the screws that hold the cover plate in place, and then remove the screws that secure the outlet to the electrical box. Carefully pull the outlet out of the box, being careful not to damage any of the wiring.
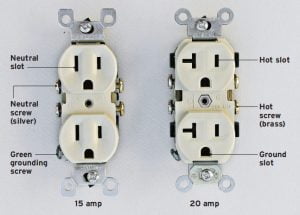
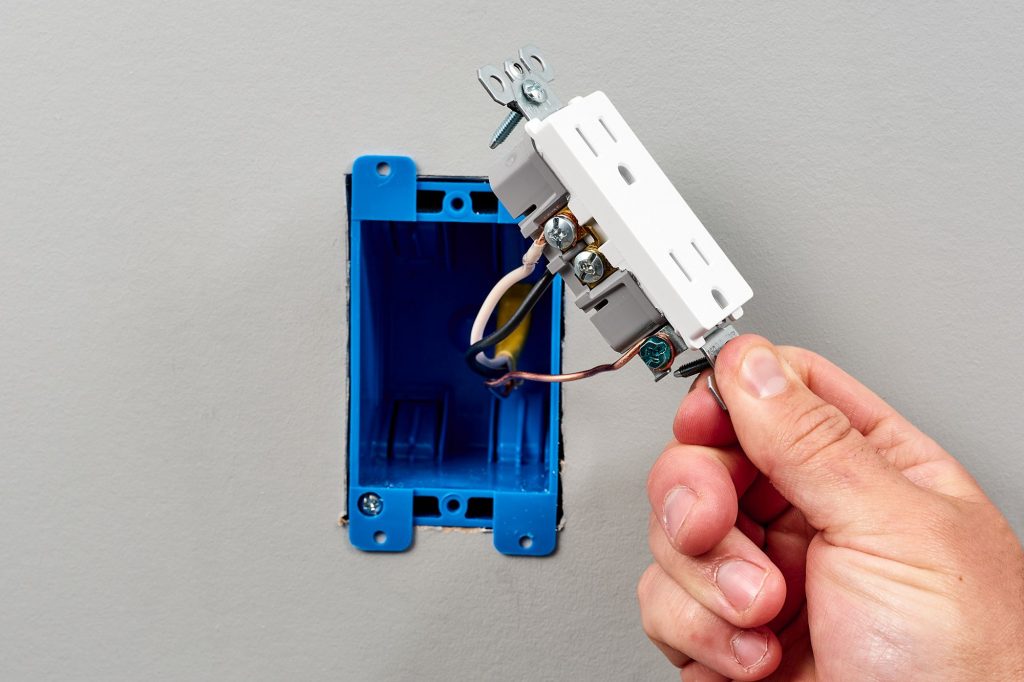
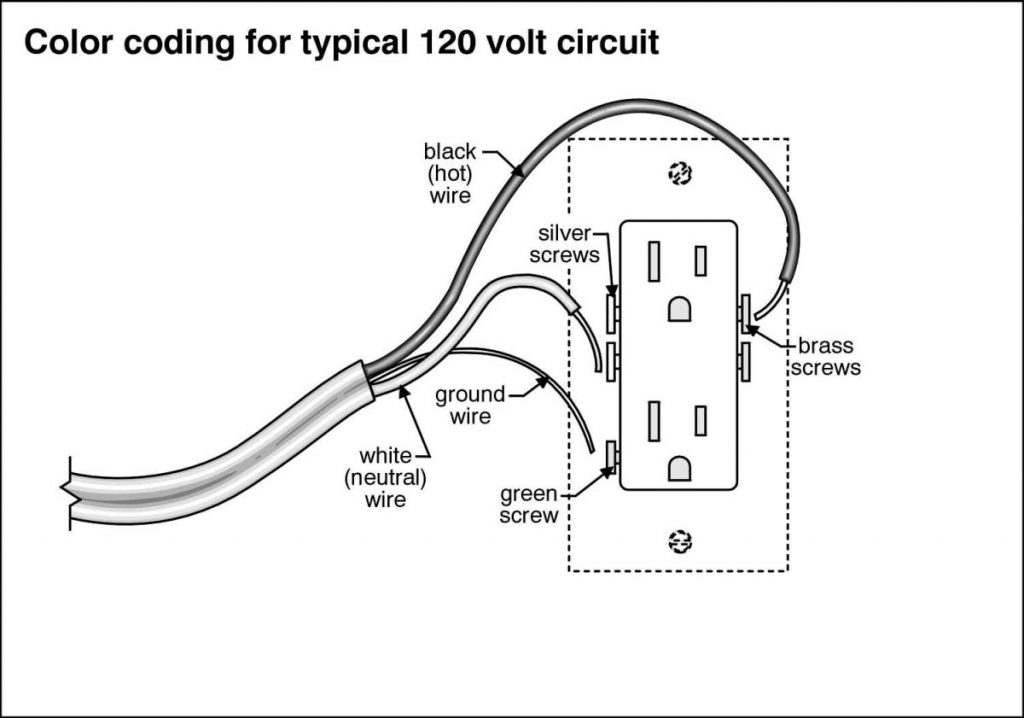
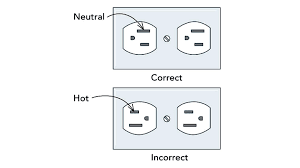
With the old outlet out of the way, it’s time to install your new one. Begin by connecting each of the hot wires (the black or red wires)to one of the brass terminals on the new outlet, and then connect each of the neutral wires (the white wires) to one of the silver terminals.
Finally, connect each of the green or copper ground wires to the screw marked with a green dot (this is usually located at either side of the outlet). Once all of the wires are connected, carefully push the outlet back into the electrical box and secure it in place with the screws provided.
If your new outlet isn’t working, don’t panic! Check out our troubleshooting tips in: How to Fix Light Switch and Outlet Issues
Troubleshooting Tips
Tips related to: how to replace an outlet, open neutrals, AC power how to replace a switch
If the power to your outlet is not working, the first thing you should do is check the breaker box. The breaker may have tripped, preventing power from flowing to the outlet. To reset the breaker, simply flip the switch to the “off” position and then back to the “on” position.
If the breaker is not tripped and the power is still not working, you’ll need to inspect the wiring. First, remove the faceplate of the outlet and check for loose or damaged wires. If everything looks okay, tighten any loose connections and reattach any loose wires. If you see any damage to the wire insulation or wires that are frayed or broken, you’ll need to replace them.
Once you’ve replaced any damaged wires and made sure all connections are tight, it’s time to test your new outlet. First, turn on the power at the breaker box and then plug a lamp into your new outlet. If it doesn’t work, double-check your wiring and make sure all connections are secure before trying again.
Component Identification Gallery
FAQs
How does AC differ from DC?
Direct current (DC) is an electric current that flows in one direction only. This means that the voltage of a DC signal does not change over time. DC signals are typically generated by batteries or solar cells.
Alternating current, on the other hand, is generated by power plants and flows through the power grid to homes and businesses. Read more..
What is Ohm’s Law?
Ohm’s law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points. In other words, the higher the voltage, the higher the current. Read more..
What are the benefits of AC motors?
AC motors are more efficient than DC motors and can operate at higher speeds. Additionally, AC motors are less likely to overheat than DC motors and can be used in a variety of applications. Read more..