Understanding GFCI’s
What is a GFCI?
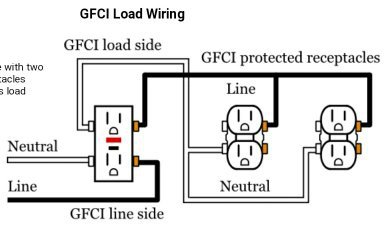
Understanding GFCI outlet wiring line vs load – A GFCI outlet is an electrical outlet that helps to protect against shock hazards. It does this by monitoring the line and load currents and shutting off the power if it detects a difference between them.
This can happen if the line current leaks to the ground, such as through a person who is touching a grounded object or an overload.
GFCI outlets are required in many areas of the home, such as near sinks and in outdoor areas. They can be installed in new construction or added to existing outlets.
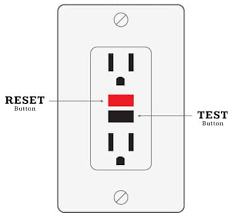
GFCI outlets have test and reset buttons that should be used regularly to ensure they are working properly.
GFCI vs Breaker
When it comes to electrical safety, there are two important terms that you need to know: breaker and GFCI.
A breaker is a device that interrupts the flow of electricity in the event of an overload. This helps to prevent fires and other damage by shutting off the power before it can cause any harm.
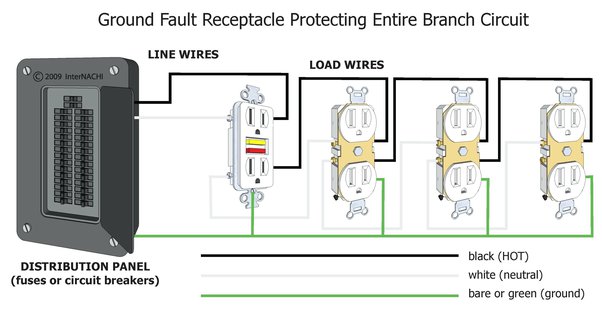
A GFCI, or ground fault circuit interrupter, is a similar device that is designed to protect against electrical shocks. In the event of a short circuit or other problem, a GFCI will quickly shut off the power, helping to prevent serious injury.
Both breakers and GFCIs are important for ensuring electrical safety. Read: AFCI vs GFCI to understand arc faults and ground faults.
GFCI Line vs Load
In order to understand the difference between line and load on a GFCI, it is first important to understand what it is.
A GFCI, or ground fault circuit interrupter, is a type of electrical outlet that is designed to protect against electrical shock.
It does this by monitoring the electricity flowing through the outlet and shuts off the power if it detects an imbalance. This imbalance can occur if there is a break in the circuit or if there is leakage to ground.
Now that we know what a GFCI is, let’s take a look at line and load:
- The “line” side of a GFCI refers to the incoming power
- The “load” side refers to any devices that are plugged into the outlet.
In order for the GFCI to work properly, both the line and load sides must be connected. If there is an imbalance on the line side, the GFCI will shut off the power to prevent electrical shock.
Where to Use a GFCI
- Bathrooms
- Kitchens
- Laundry Rooms
- Wet or damp places
- Crawlspaces
- Basements
- Garages
How to Wire a GFCI
While wiring a GFCI receptacle may seem daunting, it’s actually a fairly simple process. Here’s how to do it:
- Turn off the power to the circuit you’ll be working on.
- Remove the old receptacle and grab your new GFCI
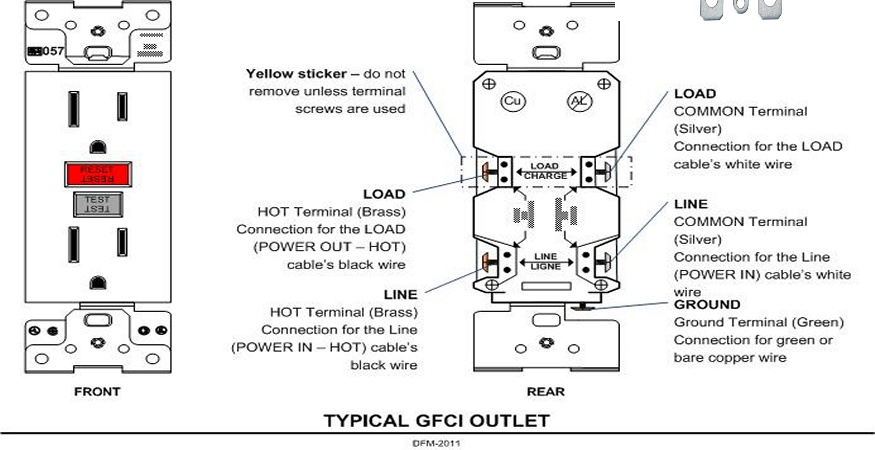
- Connect the black line (hot) wire to the Brass terminal marked “LINE,”
- Connect the white line (neutral) wire to the Silver terminal marked “LINE,”
- Connect the black load (hot) wire to the Brass terminal marked “LOAD”
- Connect the white load (neutral) wire to the Silver terminal marked “LOAD”
- Connect the ground wire to the Green terminal marked “GROUND.”
Next, attach the new receptacle to the electrical box and screw it in place.
Finally, turn on the power and test the receptacle to make sure it’s working properly.
How to Test
Testing a GFCI is simple and only takes a few minutes. Start by plugging a lamp into the outlet. Then, press the “test” button on the GFCI. The power should shut off and the lamp should go out. If it doesn’t, then the GFCI needs to be replaced. Once you’ve confirmed that the GFCI is working properly, be sure to press the “reset” button before using the outlet again.
Owning a multimeter or a plug tester are greatly encouraged for testing electrical circuits correctly
Useful Resources
What Is AC Power: Alternating Current
How to Fix Light Switch and Outlet Issues
Switch replacement and wiring conversions
FAQs
How does an AFCI work?
AFCIs work by sensing when an arc fault is about to occur and then interrupting the flow of electricity before the arc can form. Read more..
What is a rectifier?
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification. Read more..
What is direct current?
Direct current (DC) is an electric current that flows in one direction only. DC is the kind of current produced by batteries, fuel cells, and solar panels. Read more..